Australia, often thought of as a country, stretches its boundaries to encompass an entire continent known as Oceania. Yes, you read that right! This extraordinary landmass stands as the crown jewel of Oceania—a fact that will have you rethinking everything you thought you knew about Australia.
Australia, officially named ‘The Commonwealth of Australia‘, is a federation consisting of six states and two self-governing territories. Its vastness spans 7.688 million square kilometres, making it a true geographical marvel and the world’s sixth-largest country, with a contemporary population of about 25.69 million as of 2023.

Known for its expansive deserts to lush rainforests, its landscapes and wildlife are as diverse as they are breathtaking, making it a desirable destination for migrants seeking a new start. Let us jump right in and explore the things to know before migrating to Australia that will help make your move to Australia a breeze!
Where is Australia located on the world map?
Australia is situated in the southern hemisphere and occupies an entire continent. The Indian Ocean surrounds it to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the east, and the Southern Ocean to the south. In terms of its position relative to the equator, Australia’s northernmost point, the Cape York Peninsula in Queensland, is located around 10 degrees south of the equator. The southernmost point, South Point on Wilsons Promontory in Victoria, lies approximately 39 degrees south.
What are the neighbouring countries in Australia?
The country’s maritime connections include the Timor Sea and the Arafura Sea in the north, linking it with Indonesia and East Timor. Australia lacks land borders with its immediate neighbours but shares maritime boundaries with countries like Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, and East Timor. While not directly adjacent, New Zealand is relatively nearby to the southeast, separated by the Tasman Sea.
Australia boasts a diverse geography that encompasses the iconic Great Barrier Reef in the northeast and the rugged beauty of the Outback. With sweeping beaches along its coastline and vast deserts, lush rainforests, and towering mountain ranges inland, its natural wonders are truly remarkable.
What is the climate like in different regions of Australia?
Australia exhibits diverse climate zones. Northern areas like Queensland experience a monsoonal climate with distinct wet and dry seasons. Moving down the east coast to New South Wales and Victoria reveals a temperate climate boasting four seasons. Western and South Australia’s southwestern regions have a Mediterranean climate, with hot, dry summers and cooler, wetter winters. Inland areas, including the iconic Outback, endure harsh summers, cold winters, and minimal rainfall. Tasmania, in the south, features a temperate maritime climate with mild summers, cold winters, and variable weather patterns.
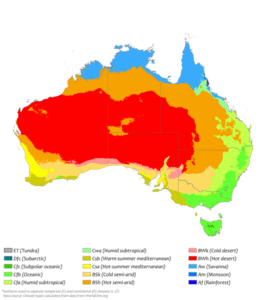
Australia’s varied climate is influenced by its vast size, diverse landscapes, and proximity to ocean currents. The weather patterns can fluctuate dramatically throughout the year in each region. For instance, northern regions experience a wet season during the Australian summer (November to April) with heavy rains, while southern regions have their wettest period during the winter months. Coastal areas benefit from the moderating effect of the surrounding oceans, resulting in milder temperatures compared to inland areas, which often experience more extreme temperature variations. Melbourne’s unique weather phenomenon of experiencing “four seasons in one day” surprises both visitors and locals.
Extreme Weather Conditions or Natural Hazards in Australia
Australia’s reputation for extreme weather and natural hazards includes bushfires during hot, dry summers, cyclones with heavy rain and winds in the north, and floods from rainfall or cyclones, particularly in low-lying areas. Droughts are common in the interior, while diverse weather patterns can bring extreme heat, heavy rain, or snowfall to different regions. It is important to be informed about weather conditions before moving to Australia in order to be prepared and ensure safety in the country’s ever-changing climate.
What are the main languages spoken in Australia?
English is the predominant language spoken in Australia, serving as the official language and the primary mode of communication across the country. Over 72% of the population speaks English as their first language, encompassing both native English speakers and those who have acquired proficiency in English as a second language. Australian English has its unique characteristics, including accent and vocabulary influenced by the country’s history and multiculturalism.
Apart from English, many Australians also speak languages other than English at home. Some of the most spoken languages in Australia, besides English, include:
- Mandarin
- Arabic
- Italian
- Greek
- Cantonese
- Vietnamese.
These languages reflect the cultural heritage and backgrounds of various communities residing in Australia, contributing to the rich linguistic tapestry of the nation.
What cultural distinctions exist between cities and regions in Australia?
Australia’s cities and regions are marked by cultural nuances that reflect the nation’s diverse tapestry. Sydney, as a global icon, pulsates with a fast-paced urban rhythm, celebrated for its stunning harbour, multiculturalism, and dynamic arts scene. Melbourne, a cultural haven, boasts a labyrinth of laneways adorned with street art, a thriving coffee culture, and a penchant for fashion and creativity.
Brisbane embraces its subtropical setting, fostering an outdoor lifestyle and a friendly, relaxed vibe. Perth, the remote gem in western Australia, connects with the Indian Ocean, encapsulating a laid-back beach culture, while Adelaide’s wine regions and festivals intertwine with a serene pace of life. Darwin embodies the spirit of the tropical north, rich in Indigenous culture and influenced by its unique environment, while Hobart, nestled in Tasmania’s embrace, resonates with historic charm amid captivating natural landscapes.
The Most Popular City and Urban Centers to Note in Australia
Sydney and Melbourne take centre stage as Australia’s most popular city, an international beacon characterised by iconic landmarks like the Sydney Opera House and a diverse cultural scene. However, Brisbane, Perth, Adelaide, Canberra, and Darwin share the limelight, with each contributing its distinct blend of lifestyle, culture, and opportunities. Together, these cities paint a vibrant mosaic of Australia’s urban landscape, offering an array of experiences that collectively define the nation’s dynamic character.
What are the Australian traditional and popular dishes?
Aussie cuisine features iconic dishes like meat pies, Vegemite on toast, and modern favourites like barramundi and kangaroo steak. Desserts like pavlova and Tim Tams are cherished treats. Cuisine in Australia varies across regions, with coastal areas known for seafood dishes, the Outback showcasing bush tucker ingredients, Asian influences prominent in cities, European flavours reflecting heritage, fusion cuisine blending indigenous ingredients, and wine regions offering culinary experiences.


Are there any specific dietary considerations or unique ingredients used in Australian cooking?
Australian cuisine accommodates diverse dietary needs like vegetarian, vegan, gluten-free, and lactose-free while incorporating indigenous “bush tucker” ingredients such as wattle seed, lemon myrtle, quandong, and macadamia nuts. Seafood, including barramundi and prawns, is prominent due to the extensive coastline. Native fruits, berries, and macadamia nuts enhance both sweet and savoury dishes, showcasing Australia’s culinary diversity and unique ingredients.
What food places are common in Australia, and how can new migrants find familiar foods from their home country?
Australia’s dining scene is rich and varied, especially in urban areas, offering everything from fine dining to casual cafes, international cuisine, and vibrant street food from food trucks and markets. Pubs and gastropubs are favourites for hearty meals and drinks, while the multicultural population ensures a diverse range of specialty restaurants and grocery stores showcasing flavours from around the world.
New migrants in Australia can find familiar foods through ethnic grocery stores, multicultural neighbourhoods with diverse restaurants and specialty shops, and online platforms offering international ingredients. Engaging with community networks, attending food festivals, and utilising e-commerce sites can help migrants connect with their cultural communities and embrace their culinary heritage while adjusting to living in Australia.
What are the must-visit places in Australia?
Australia is a vast country blessed with captivating destinations that beckon travellers from all corners of the globe. From iconic landmarks to natural wonders, here are some must-visit places that showcase the splendour of Australia.
- Sydney Opera House and Sydney Harbour Bridge
- Great Barrier Reef
- Uluru (Ayers Rock)
- The Great Ocean Road
- The Daintree Rainforest
- Northern Territory’s Kakadu National Park
- Fraser Island, part of the Great Sandy National Park
- The Blue Mountains National Park
- Kangaroo Island
What sports and outdoor activities are commonly enjoyed in different regions of Australia?
Aussie adoration for sports and nature is deeply ingrained, forging a link between its diverse regions and the passions of its people. Coastal stretches invite surfers to ride the waves while bushwalkers explore terrain that shifts from rugged to serene. Sailing finds a home in iconic harbours, and cricket and rugby awaken the national spirit.
Beneath the waves, snorkelling and diving unveil a hidden aquatic world, and winter brings skiing and snowboarding to the forefront. Rock climbing challenges and tranquil camping experiences complete the picture as Aussies embrace their nation’s extensive playground, fostering a deep connection with the land and the heartening pursuit of outdoor activities.
What are the public transportation options?
Australia offers a comprehensive public transportation network that facilitates convenient travel across cities and regions. Major cities like Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, and Adelaide have well-developed public transport systems, including trains, buses, trams and ferries, allowing residents and visitors to move seamlessly within urban areas.
Transportation options differ across various regions of Australia due to factors like population density, geography, and urban planning. In large cities, there is a comprehensive public transport network that facilitates effective commuting. Smaller towns might offer fewer public transport alternatives, leading to a higher dependence on private vehicles due to larger gaps between destinations and limited public transport routes. In isolated and rural areas, access to public transport is very hard, making personal vehicle usage more crucial for daily routines. It is important to research transportation options before moving to a new area to ensure you can travel comfortably and effectively based on the local infrastructure and services available.
How can I obtain a driving license in Australia?
Prior to relocation, it’s crucial to understand the public transportation network of your chosen city to navigate effectively. Furthermore, if you intend to drive in Australia, securing a driving license is vital. The procedure generally encompasses the following stages:

- Learner’s Permit: First, you need to apply and acquire a learner’s permit, which allows supervised driving practice. The specific requirements can differ based on the state or territory.
- Practice Period: Fulfill a set number of supervised driving hours, adhering to guidelines set by the local licensing authority.
- Driving Test: Once you’ve gained adequate experience, take a driving test to demonstrate your road skills and rule knowledge. Passing leads to a provisional (P) license.
- Provisional License: Provisional licenses have various stages, each with its own rules like passenger limits and night driving constraints.
- Full License: After completing the required provisional period without infringements, you can apply for an unrestricted full driving license.
What are the living conditions like in Australia?
Living conditions in Australia are generally considered to be of high quality, offering a comfortable lifestyle. The country boasts accessible healthcare, well-developed educational institutions, and modern infrastructure. Australian cities are known for their safety, cleanliness, and well-planned urban spaces. Housing options vary, ranging from city apartments to suburban homes, catering to different preferences and budgets.
Australia offers abundant job opportunities and places a strong emphasis on achieving a balanced work-life dynamic, which contributes to a healthy and fulfilling lifestyle. The country’s multicultural society warmly welcomes migrants, fostering cultural integration and embracing diversity. For students, it is essential to consider living expenses, which can vary based on factors like location and lifestyle choices. The cost of living in Australia encompasses accommodation, transportation, groceries, healthcare, and entertainment. It’s important for students to budget and plan accordingly to ensure a comfortable and financially manageable experience.
To fully embrace the Australian way of life, new migrants, including students, should focus on developing English language skills, learning about Australian customs and values, building networks, and actively participating in community events and activities. These steps will help facilitate a smooth transition and foster a sense of belonging in Australian society.
How does the lifestyle differ across various cities and regions?
Australia’s cities and regions offer diverse lifestyles influenced by factors such as climate, culture, and geography. Urban centres like Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane each have their distinct vibes, catering to different preferences. There is more to life than cities on the West Coast, such as Perth and Adelaide, offering unique beach-oriented and relaxed lifestyles. Australia’s rural areas provide tranquillity and a connection to nature, while remote and outback communities thrive on their own self-sufficiency and a strong sense of community. Choosing a location that aligns with your lifestyle aspirations ensures a rewarding experience in Australia’s rich tapestry of opportunities and environments.
What are the healthcare options, and how does the medical system function?
Australia has a healthcare system that is funded by both the Australian Government and private health insurance. The public healthcare system in Australia is known as Medicare, which offers healthcare services to Australian residents either for free or at a reduced cost. Under Medicare, individuals have access to a wide range of medical services, including doctor’s visits, hospital care and prescription medications.

Healthcare costs in Australia are funded partly through resident taxes. Citizens pay a 2% Medicare Levy on their income, sustaining the public healthcare system. Additionally, private health insurance is available for those seeking extra medical services or treatment in private hospitals. This dual approach, combining public and private elements, guarantees comprehensive and accessible healthcare throughout Australia.
Where does Australia’s economy rank globally?
In the landscape of global economies, Australia stands as a highly developed nation with a diverse and thriving economic landscape. As of 2023, Australia proudly holds the title of the 13th-largest national economy by nominal GDP and the 19th-largest by PPP-adjusted GDP. Moreover, its prowess is evident in its position as the 20th-largest goods exporter and the 24th-largest goods importer on the world stage.
The growth of Australia’s economy has been driven by key sectors, including the mining and resources industry with abundant reserves of minerals like iron ore and natural gas, the services sector encompassing finance, tourism, education, and healthcare, as well as the agricultural sector producing products like wheat, beef, wool, and wine. Technological advancements and innovation across these sectors have further contributed to economic diversification and global competitiveness.
What is the unemployment rate, and how can one find job opportunities?
The unemployment rate serves as a key indicator of economic health, reflecting the percentage of the labour force actively seeking employment but unable to secure it. As per the Australian Bureau of Statistics(ABS), Australia’s unemployment rate stands at 3.6% (May 2023), showcasing a relatively stable employment environment. This figure not only provides insight into the labour market’s vibrancy but also offers valuable information for workforce planning and policy formulation.

With an increase in employment rate, job seekers can enhance their employability by continuously upgrading their skills through education and training, building a robust professional network, and leveraging online job search platforms. Recruitment agencies, industry associations, and government resources also play pivotal roles in connecting individuals with suitable roles.
How can migrants have their foreign qualifications recognised in Australia?
Migrants can have their foreign qualifications recognised in Australia through official channels. They can approach government agencies like the Australian Skills Recognition Information(ASRI) and Professional Recognition in Australia (PRA) program. These bodies assess overseas qualifications and compare them to Australian standards, enabling migrants to demonstrate their credentials to potential employers and educational institutions.
What are the typical working conditions, such as hours, holidays, and benefits, in Australia?
Working Hours:
- Full-time: The standard workweek is 38 hours over 5 days.
- Part-time: Hours vary based on agreements.
- Shift Work: Shifts might include evenings, nights, or weekends.
Holidays:
- Paid Annual Leave: Employees receive 4 weeks per year (pro-rata for part-time).
- Public holidays: These vary by state and territory.
Benefits:
- Paid sick leave.
- Maternity/paternity/adoption leave.
- Mandatory superannuation: Employers contribute 10% of earnings for retirement funds who do not intend to retire in Australia.
- Medicare healthcare system.
- Workplace safety regulations.
- Possible flexible work arrangements.
What are Australia’s in-demand professions, and how can migrants access career counselling or job placement services?
In Australia, there is a current demand for professionals in industries such as healthcare, information technology, engineering, trades and construction, education, and aged care. These sectors offer significant job opportunities owing to factors like population growth, technological advancements, and evolving societal needs.

Migrants seeking to access these career opportunities can utilise various avenues for career counselling and job placement services. Government-funded programs like the Department of Home Affairs’ AMEP (Adult Migrant English Program) often include career guidance. Non-profit organizations, community centres, and online platforms provide workshops, counselling, and resources tailored to migrants’ career needs, assisting them in effectively navigating the Australian job market and finding suitable employment opportunities.
How is the education system structured in Australia?
Australia’s education system is renowned for its quality and diversity, providing a comprehensive framework for students from early childhood through tertiary education. The system is divided into several stages:
- Early Childhood Education:
- Age: 0-5 years
- Includes preschool and kindergarten programs focused on foundational learning and development.
- Primary School:
- Age: 6-12 years
- Consists of six grades, typically from Year 1 to Year 6, focusing on core subjects.
- Secondary School:
- Age: 12-18 years
- Divided into two stages: junior secondary (Years 7-10) and senior secondary (Years 11-12).
- Students in Year 12 take the Higher School Certificate (HSC) or the Victorian Certificate of Education (VCE), which are recognised for university admission.
- Tertiary Education:
- Age: 18+ years
- Includes universities, vocational education and training (VET), and technical and further education (TAFE) institutions.
- Offers bachelor’s degrees, vocational qualifications, and postgraduate studies.
With a quality education system, Australia offers diverse schooling options for children. Schooling options vary, including public schools (government-funded), private schools (independent and Catholic), and international schools. Homeschooling and special education schools are also available, catering to specific needs and preferences. This range of choices empowers parents to select the best fit for their children’s education. Australian education prioritises inclusivity and high standards, making it an attractive destination for international students as well.
What is the crime in Australia?
According to the latest ABS crime figures, the offender rate in Australia for 2020/21 was 1,599 criminals per 100,000 people, which is a decrease of 78 from the previous year. This indicates that Australia is becoming safer over time. In 2020-21, the police department prosecuted 359,975 offenders, which is a 4% decline from the previous year’s 413,025 prosecutions.
Australia boasts relatively low crime rates compared to many other countries, although regional variations exist. Major cities like Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane tend to have higher crime rates than smaller towns and rural areas. Property crimes, such as theft and burglary, are among the most common offences, along with certain types of assaults.
However, if you are thinking about moving to Australia as a new immigrant, you need to prioritise safety by understanding local laws and regulations to avoid legal issues. Being cautious, especially in cities, involves using well-lit areas, safeguarding belongings and avoiding isolated places at night. Awareness of scams and seeking support from local networks or migrant services enhances security.
What is the currency of Australia?
The official currency of Australia is the Australian Dollar (AUD). It is the legal tender used throughout the country and its external territories, as well as by three independent sovereign Pacific Island states: Kiribati, Nauru, and Tuvalu. The currency is symbolised by “$”, “A$”, or “AUD” and is further divided into 100 smaller units called cents. Australian dollars are available in various denominations of banknotes, including $100, $50, $20, $10, and $5, and coins, such as 5 cents, 10 cents, 20 cents, 50 cents, $1, and $2.

Any individual travelling to Australia should note that the AUD’s value can change due to economic factors. Staying updated on exchange rates aids financial planning, independence, and avoiding scams. Understanding the Australian Dollar is crucial for a smooth financial transition and adaptation to life in Australia.
What is the political system in Australia?
Australia’s political system is a blend of constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy. The British monarch, represented by the Governor-General, holds a symbolic role, while elected representatives handle governance. The Parliament comprises two houses: the House of Representatives, where the majority party forms the government, and the Senate, which checks government power.
Australia’s federal structure encompasses six states and two territories, each with its own government handling specific areas. The Prime Minister, leader of the House’s majority party, heads the government and leads the Cabinet in policy decisions. Upholding the rule of law, an independent judiciary, particularly the High Court, interprets the Constitution and ensures the separation of powers. Political diversity thrives through major parties, like the Australian Labor Party and Liberal Party, as well as minor parties and independent representatives.
What are the legal requirements for migrants?
Migrating to Australia involves meeting specific legal requirements tailored to different visa categories. The various types of visas available require evidence of skills, qualifications, health, character and, in some cases, sponsorship or nomination. Demonstrating financial capacity and providing accurate documentation is also vital. If you are thinking of moving to Australia, it is important to know about the different visa categories available such as:
The Student Visa (Subclass 500)
Student visa permits international students to study full-time at Australian educational institutions, spanning primary school to university and vocational training. Enrolment, proof of funds, and meeting health and character criteria are essential. Visa duration aligns with course length, allowing limited work rights.
The processing time for the Student Visa (Subclass 500) varies depending on the individual case and various factors. However, according to ADH, for 75% of applications, the processing time is approximately 25 days, while for 90% of applications, it takes around 68 days. The visa application fee for the Student Visa (Subclass 500) is AUD 710. This fee is subject to change, so it’s advisable to check the official Australian immigration website or consult with relevant authorities for the most up-to-date information.
The Partner Visa (Subclass 820/801 or 309/100)
The Partner Visa allows partners of Australian citizens, permanent residents, or eligible New Zealand citizens to live in Australia. It comprises a two-stage process: a temporary visa leading to a permanent one. Applicants must demonstrate the authenticity of their relationship and meet health and character standards. This visa type offers a route to permanent residency.
The average processing time for the Partner Visa can vary depending on the chosen category and subclass. According to the Australian Department of Home Affairs (ADH), it typically takes about 9 months to 45 months for the visa application to be processed. The processing time can be influenced by factors such as the complexity of the case, the completeness of the application, and the workload of the immigration department. The cost of the visa can vary depending on the specific circumstances and subclass chosen. The fees for the Partner Visa range from AUD 1475 to AUD 8850.
Read more: Partner Visa Application Checklist
Skilled Visa (Subclass 189, 190, 491)
Skilled Visas are for those with sought-after skills in Australia. Subclass 189 is independent, subclass 190 needs state/territory nomination and subclass 491 is regional. Applicants submit an Expression of Interest (EOI) and then provide proof of skills, work experience, and language proficiency upon invitation.
As per ADH, the processing time for skilled visas can range from 3 months to 30 months on average, although it can vary depending on factors such as case complexity, documentation accuracy, and immigration department workload. For the Subclass 491 visa sponsored by an eligible family member, approximately 90% of applications are processed within 19 months, but individual circumstances can cause variations in this timeframe, and the cost for skilled visas is AUD 4640.
The Visitor Visa (Subclass 600)
The Visitor Visa provides individuals with the opportunity to have short-term stays in Australia for purposes such as tourism, business activities, or visiting family and friends. It encompasses different streams, including tourist, business, sponsored family, and approved destination status. Applicants must demonstrate genuine temporary stay intentions and meet health and character standards.
The processing time for the Visitor Visa can vary, but as per ADH, for 90% of family sponsored applications, it typically takes around 66 days for the visa to be processed. It’s important to note that processing times can be influenced by factors such as the completeness and accuracy of the application, the complexity of the case, and the workload of the immigration department. The cost of the Visitor Visa depends on the specific category chosen. The fees for this visa range from AUD 190 to AUD 1395.
You may also like: How can I transition from a tourist visa to a partner visa in Australia?
Temporary Skill Shortage (TSS) Visa (Subclass 482)
TSS visa allows employers to sponsor skilled overseas workers to fill specific positions in Australia. The visa has short-term and medium-term streams, and applicants must have a valid job offer from an Australian employer. The processing time for the sponsored TSS visa can vary, but approximately 90% of applications are processed within 71 days, according to the ADH. The cost of the TSS visa depends on the specific category chosen. The fees for this visa range from AUD 14,552 to AUD 3,035.
Obtaining a visa can pose challenges like complex eligibility criteria, changing regulations, and stringent document verification. Navigating Australia’s visa system requires careful research and adherence to specific requirements for each visa category. Seeking guidance from the official Australian Government website or immigration professionals like 4Nations Internationalcan greatly assist in understanding the processes and requirements for a successful migration journey.
We, a reputable migration agency with expertise in Australian immigration, strive to make every individual’s Australian visa application successful. If you are considering migrating to Australia and need assistance with the visa application process, reach out to us today!
Global Opportunities Beckon! Discover Seamless Immigration Services.
How can family members be supported during the migration process?
Supporting family members during migration involves open communication, emotional support, practical assistance, and recognising their well-being. By staying connected, addressing concerns, and providing help with documents and settlement services, families can navigate the process together. Financial support, when possible, can ease the burdens. It’s important to prioritise emotional well-being, encourage open discussions, and seek professional help if needed. This support fosters unity and resilience during the migration journey.
What are the regulations for bringing pets to Australia?
Bringing your cherished feline or canine companion to Australia is an exciting venture, but it comes with a complex set of regulations and considerations. Before embarking on the import journey, it’s essential to determine whether your pet is eligible for import. Certain cat and dog breeds may not be allowed due to specific health and safety concerns. You are not permitted to import pets to Australia without fulfilling certain requirements, such as rabies antibody testing, microchipping and external parasite treatments.
Make sure to use a laboratory approved by the Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry for rabies antibody testing. For detailed information, you can go through The Australian Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment website to ensure a smooth and safe pet relocation process.
Why is Australia considered an attractive destination for migration?
Australia is considered an attractive destination for migration due to a multitude of factors. Its strong economy offers ample job opportunities, higher wages, and a high standard of living. The country boasts a well-developed healthcare system, excellent education options, and a diverse cultural environment. Australia’s stunning landscapes, from pristine beaches to iconic landmarks, also make it appealing.
Moreover, its safe and stable political climate, efficient infrastructure, and access to social services contribute to its allure. The Australian government’s skilled migration programs attract professionals and skilled workers, while its multicultural society embraces diversity. All these elements combine to create a welcoming and prosperous environment, making Australia a sought-after destination for those seeking a better quality of life and new opportunities.
What are the specific cultural norms and social etiquette in Australia?
Australia has a laid-back and egalitarian culture where using first names, even in professional settings, is common. Personal space is valued, and people maintain a relaxed physical distance when interacting. Punctuality is appreciated in both social gatherings and business meetings. Humour and banter play a significant role in social interactions, but it’s important to be mindful of the context and audience.
Australians value direct communication, honesty, and openness. Tipping isn’t customary, but appreciated for exceptional service. Respect for Indigenous cultures and acknowledgement of their land is important. Inclusivity, friendliness, and a relaxed approach to social interactions are appreciated.